5 steps for your first RAG setup
You're just a few clicks away from production-ready AI.
Hi there, I’m continuing my AI series with a focus on RAG today. If you don’t know why you need it or how to get started, you shouldn’t miss this.
Before we start, a quick reminder that your Early Bird Black Friday offers will be available on Educative for only one more week. This is a great opportunity to grab access to all of our courses on RAG, Agentic AI, and other critical AI topics. Use this link to view your offers.
Building with LLMs is exciting… until your app confidently tells a user that the Eiffel Tower is in Berlin.
Many developers hesitate to work with AI because of its unpredictability. And for good reason. Major hallucinations kill user trust fast.
But there’s a proven architecture to reduce those mistakes: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Instead of asking the LLM to recall an answer, RAG involves giving your LLM the context needed to generate a better answer in real time.
The result is more accurate answers, fewer hallucinations, and way better UX.
Today, I’ll cover:
How RAG actually works
How to build your first pipeline
Best practices and popular tooling
Let’s dig in.
How RAG works
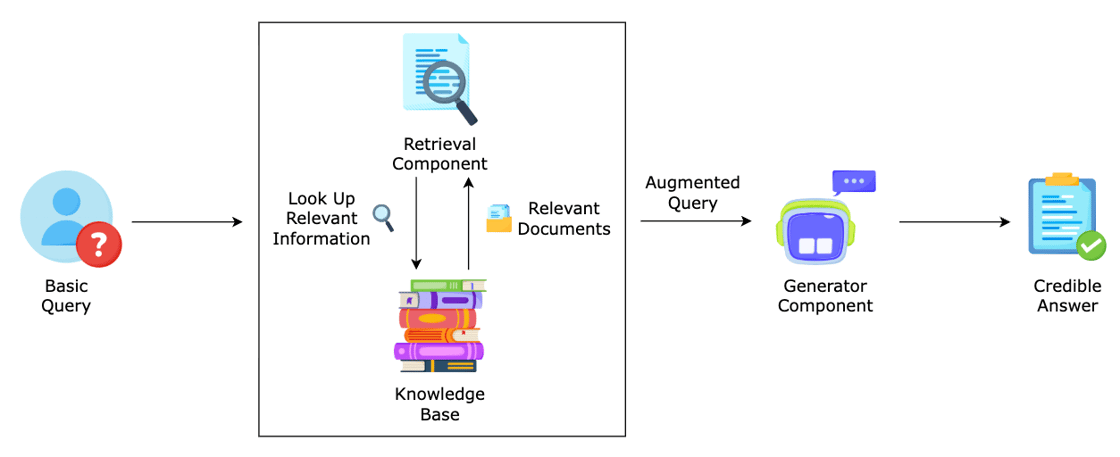
At a high level, RAG combines retrieval and generation in a tight loop. Instead of just prompting an LLM, you’re plugging it into a pipeline that feeds it curated, context-relevant info in real time.
Here’s what’s happening in a RAG-enabled system when a user submits a question:
Query comes in
The user asks something like: “What’s our refund policy for enterprise clients?”
A clear, specific question = better retrieval = better answer.
Retrieval kicks in
The system embeds the query, runs a similarity search on your vector DB, and pulls back relevant chunks of context.
Augmented prompt is built
The original question + retrieved context + instructions (e.g. “Only answer using this info. Say ‘I don’t know’ if it’s not there.”)
LLM generates the response
The model uses the prompt to generate a fluent, fact-grounded reply — now informed by your actual data.
User gets an answer they can trust
Hallucination risk drops, confidence goes up. Users get useful answers, not confident guesses.
This is the conceptual flow of RAG, but to make it real, you need a few key pieces working together. Let’s walk through how to wire them up into an actual pipeline you can ship.
Your first basic RAG pipeline
A lightweight, functional RAG stack can be built with a handful of tools and some Python glue code.
Here’s a simple version you can stand up today in 5 steps.
1. Ingest your data
You need to make your docs searchable.
That means:
Chunking them (e.g. 500-token chunks)
Converting them into vector embeddings using a model like text-embedding-3-small
🛠️ Tools: LangChain, LlamaIndex, or a simple script using OpenAI + FAISS.
2. Store your vectors
These embeddings go into a vector database, which lets you search by semantic similarity instead of keywords.
🛠️ Tools:
Open-source: FAISS, Chroma
Managed: Pinecone, Weaviate, Qdrant
3. Handle the user query
You get a user question like: “What’s the SLA for our enterprise customers?”
You embed that question the same way you did your docs, and run a similarity search against your vector DB. This pulls back relevant chunks (say, a paragraph from your internal policy doc).
4. Construct the prompt
Now you build a prompt that includes:
The user’s question
The relevant retrieved context
Instructions for how to answer (this part matters more than you think)
Example:
“Use the following context to answer the question. If the answer isn’t in the context, just say ‘I don’t know.’ Don’t make anything up.”
5. Call the LLM
You send the prompt to the model (OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, etc.) and get a response that’s:
Grounded in your actual data
Less prone to hallucination
More trustworthy for users
And congratulations, you’ve built your first RAG pipeline.
RAG best practices
The difference between a scrappy prototype and a system users can actually trust often comes down to how well you manage the details.
Here are a few principles that’ll save you hours of debugging (and some deeply unhinged LLM outputs):
Chunking size matters. Too big? You lose precision. Too small? You lose context. 300–500 tokens per chunk is a good default.
“I don’t know” prompting is critical. Tell the model not to improvise when the answer isn’t in the context. Otherwise? It will.
Eval early. Don’t wait until prod to find out your retrieval sucks. Manually check: “Does the retrieved context actually answer the query?”
Don’t overcomplicate it. You can do basic RAG with a local FAISS index, 50 lines of Python, and OpenAI’s embedding API. Tools like LangChain are great — just know what’s under the hood.
Stick to these, and you’ll avoid 90% of the most common RAG faceplants.
When NOT to use RAG
RAG is powerful, but it’s not a silver bullet.
It won’t help if:
You’re doing complex reasoning across multiple documents (that’s better for agents or multi-step planners)
You need structured data from APIs or databases (use tools instead)
Your data is always changing in real-time (consider hybrid approaches)
And if RAG doesn’t fit your use case, there are alternative approaches you could take:
Tool use and API calling for tasks that rely on dynamic or structured data,
Fine-tuning might be more efficient if your domain is stable but highly specific.
A hybrid approach — using RAG where flexibility is needed, and fine-tuning or tools where precision matters.
Ground your models now, thank yourself later
If your app needs to ground its answers in real knowledge, you definitely need to learn RAG.
But don’t get blocked by tooling or perfectionism. Just build a scrappy prototype, test it with real users, and improve it from there.
The sooner you start, the sooner you stop shipping AI that just makes stuff up.
Here are some resources to help you get started:
👉 New to RAG? Fundamentals of Retrieval-Augmented Generation with LangChain shows you how to apply LangChain to implement RAG pipeline and build a frontend app for your pipeline with Streamlit.
👉 Ready for advanced RAG? Advanced RAG Techniques: Choosing the Right Approach covers different RAG approaches, post-retrieval optimization methods, and designing RAG-based chatbots.
This is your last week to access these courses and more at 50% off (or more) for our Early Bird Black Friday Sale.
Next week, we’ll demystify agents and how you can grok them to future-proof your career.
Any questions about the future of development or AI? Leave a comment and let me know.
Happy learning!
- Fahim